(*如果之後架構有變,這邊不會更新)
來聊聊OpenBMC的Redfish怎麼快速上手, 如果對redfish沒有很熟的話,可以先看"認識Redfish"裡面講解的概念
Code 在哪裡?
Redfish的Code 是放在bmcweb這一包裡面
GitHub - openbmc/bmcweb: A do everything Redfish, KVM, GUI, and DBus webserver for OpenBMC
目前OpenBMC的Web打算採用前後端分離的方式,後端是Redfish,前端是webui-vue,所以我猜bmcweb這個名字是這樣來的
如何開始? 該先看哪隻程式碼?
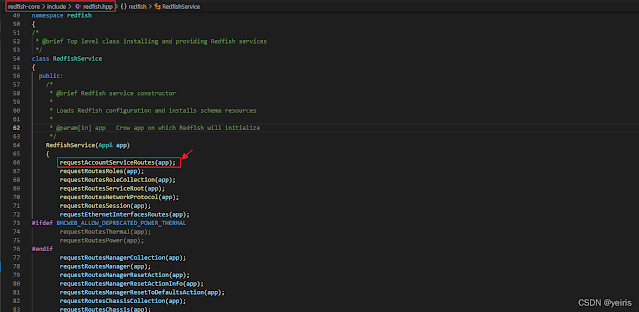
Redfish Service
在src\webserver_main.cpp 中將RedfishServices加到router
RedfishServices (redfish-core\include\redfish.hpp)裡面有很多sub router
這些subrouter定義的程式碼都在"redfish-core\lib\"資料夾底下,以requestAccountServiceRoutes為例,定義在account_service.hpp中
使用者權限(privileges)
根據Redfish Spec的描述,User Role有三種可以選擇Administrator, Operator 和ReadOnly
這邊還是以AccountService的redfish::privileges::getAccountService為範例,在redfish-core\include\registries\privilege_registry.hpp可看到
// AccountService
const static auto& getAccountService = privilegeSetLogin;其中privilegeSetLogin 是Login 權限,所以Administrator, Operator 和 ReadOnly User都可以GET /redfish/v1/AccountService/
namespace redfish::privileges
{
// clang-format off
const std::array<Privileges, 1> privilegeSetLogin = {{
{"Login"}
}};
const std::array<Privileges, 1> privilegeSetConfigureComponents = {{
{"Conf
...redfish-core\lib
這個資料夾中存放了所有support 的redfish resource的程式碼,可以先看自己要研究的API,例如常見的ComputerServices
//redfish-core\lib\systems.hpp
BMCWEB_ROUTE(app, "/redfish/v1/Systems/system/")
.privileges(redfish::privileges::getComputerSystem)
.methods(
boost::beast::http::verb::
get)([](const crow::Request&,
const std::shared_ptr<bmcweb::AsyncResp>& asyncResp) {}資料操作皆來自Dbus
什麼是Dbus
OpenBMC提供了介紹影片,我覺得講得很完整 sdbusplus & phosphor-dbus-interface - YouTube
OpenBMC是由很多個daemon所組成的,像是ipmid, fwupd, fscd等,dbus可以想像成他們的共享資料夾,所以當我們要修改資料或是拿取資料的時候,就去dbus相對位置拿取就可以了,底下是我在維基看到的圖片,從圖片中可以感受到有了Dbus之後,Daemon間的溝通變得簡單有條理
Dbus的組成有三個元素:
Service - A daemon attached to the dbus and providing objects.
root@romulus:~# busctl xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC
Object Paths – A tree, like a file system, of paths to objects.(對象路徑的樹,如文件系統)
root@romulus:~# busctl tree xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC
└─/xyz
└─/xyz/openbmc_project
└─/xyz/openbmc_project/state
└─/xyz/openbmc_project/state/bmc0Interface – The 'class' of an object. Objects support multiple inheritance.(對象的“ class ”。 對象支持多重繼承)
- Property – Store values. Some can be written to (存儲值。有些可以改寫)
- Method – Make method calls.(進行方法調用)
- Signal – Inform other process about an event. (將事件通知其他進程)
root@romulus:~# busctl introspect xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC /xyz/openbmc_project/state/bmc0 NAME TYPE SIGNATURE RESULT/VALUE FLAGS xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC interface - - - .CurrentBMCState property s "xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC.BMCState… emits-change writable .LastRebootTime property t 1619401752000 emits-change writable .RequestedBMCTransition property s "xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC.Transiti… emits-change writable
所以如果Redfish 想要取得BMC的LastRebootTime,那他就要下get-property指令
get-property ... SERVICE OBJECT INTERFACE PROPERTY
// 這個指令是下在bmc console 中的 busctl get-property xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC /xyz/openbmc_project/state/bmc0 xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC LastRebootTime
那在程式碼實作就是如下,可以看到他在get-property 的function中分別帶入service, object ,interface和property
//redfish-core\lib\managers.hpp
inline void
managerGetLastResetTime(const std::shared_ptr<bmcweb::AsyncResp>& aResp)
{
BMCWEB_LOG_DEBUG << "Getting Manager Last Reset Time";
sdbusplus::asio::getProperty<uint64_t>(
*crow::connections::systemBus, "xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC",
"/xyz/openbmc_project/state/bmc0", "xyz.openbmc_project.State.BMC",
"LastRebootTime",
[aResp](const boost::system::error_code ec,
const uint64_t lastResetTime) {
if (ec)
{
BMCWEB_LOG_DEBUG << "D-BUS response error " << ec;
return;
}
// LastRebootTime is epoch time, in milliseconds
// https://github.com/openbmc/phosphor-dbus-interfaces/blob/7f9a128eb9296e926422ddc312c148b625890bb6/xyz/openbmc_project/State/BMC.interface.yaml#L19
uint64_t lastResetTimeStamp = lastResetTime / 1000;
// Convert to ISO 8601 standard
aResp->res.jsonValue["LastResetTime"] =
crow::utility::getDateTimeUint(lastResetTimeStamp);
});
}回調函數(Callback function)
回調函數(callback function)是指能藉由參數(argument)通往另一個函數的函數。例如底下範例
//sdbusplus/include/sdbusplus/asio/connection.hpp
void async_method_call(MessageHandler&& handler, const std::string& service,
const std::string& objpath,
const std::string& interf, const std::string& method,
const InputArgs&... a)在 async_method_call 中,先註冊了MessageHandler&& handler 這個回調函數,因此在Dbus 的回覆回傳時,就會執行我們註冊的MessageHandler&& handler
前面有提到Redfish所有資料都是來自於Dbus,因此我們必須在Dbus回復回傳的時候,才能Response StatusCode,所以我們在Redfish中可以看到大量Callback function的用法
例如AccountService/Accounts的PATCH Method,在Dbus回覆之後,便執行註冊的callback function
//redfish-core\lib\account_service.hpp
BMCWEB_ROUTE(app, "/redfish/v1/AccountService/Accounts/<str>/")
.privileges({{"ConfigureUsers"}, {"ConfigureSelf"}})
.methods(boost::beast::http::verb::patch)(
[](const crow::Request& req,
const std::shared_ptr<bmcweb::AsyncResp>& asyncResp,
const std::string& username) -> void {
//verify value, 先省略掉
crow::connections::systemBus->async_method_call(
//callback function start
[asyncResp, username, password(std::move(password)),
roleId(std::move(roleId)), enabled,
newUser{std::string(*newUserName)},
locked](const boost::system::error_code ec,
sdbusplus::message::message& m) {
if (ec)
{
userErrorMessageHandler(m.get_error(), asyncResp,
newUser, username);
return;
}
updateUserProperties(asyncResp, newUser, password,
enabled, roleId, locked);
}
//callback function end
,
"xyz.openbmc_project.User.Manager",
"/xyz/openbmc_project/user",
"xyz.openbmc_project.User.Manager", "RenameUser", username,
*newUserName);
});那如果有很多Dbus method需要依序呼叫的時候,就會發現有巢狀回調函數的出現,這樣可以執行完一個method後再call 下一個mthod
crow::connections::systemBus->async_method_call(
[asyncResp](const boost::system::error_code ec,
sdbusplus::message::message& m) {
if (ec)
{
return;
}
crow::connections::systemBus->async_method_call(
[asyncResp](const boost::system::error_code ec,
sdbusplus::message::message& m) {
if (ec)
{
return;
}
crow::connections::systemBus->async_method_call(
[asyncResp](const boost::system::error_code ec,
sdbusplus::message::message& m) {
if (ec)
{
return;
}
updateUserProperties(asyncResp, newUser, password,
enabled, roleId, locked);
},
"Service 3",
"object path3",
"Interface", "method", value, value'
);
},
"Service 2",
"object path2",
"Interface", "method", value, value'
);
},
"Service 1",
"object path",
"Interface", "method", value, value'
);如果掌握以上幾點再去看bmcweb的code,會發現其實也沒這麼複雜




沒有留言:
張貼留言
注意:只有此網誌的成員可以留言。